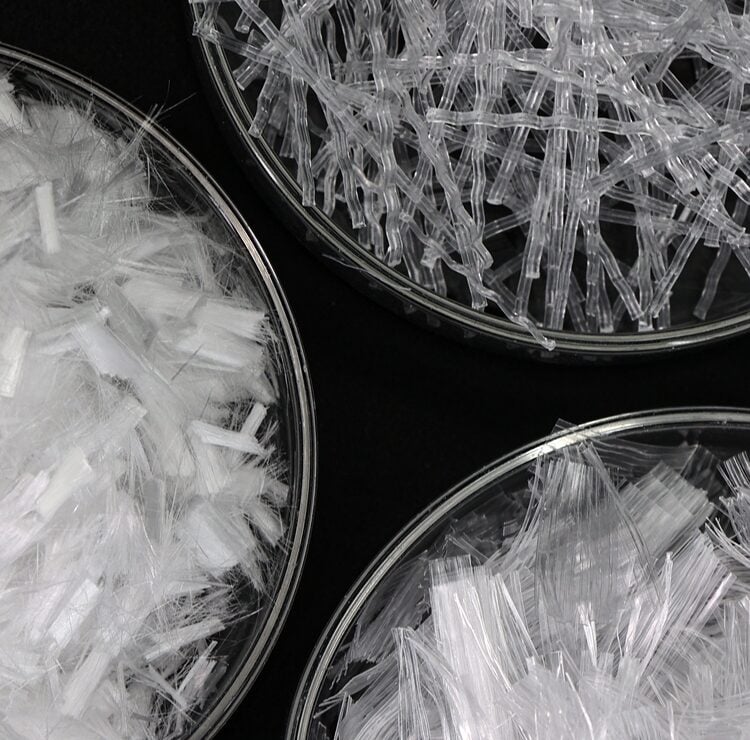
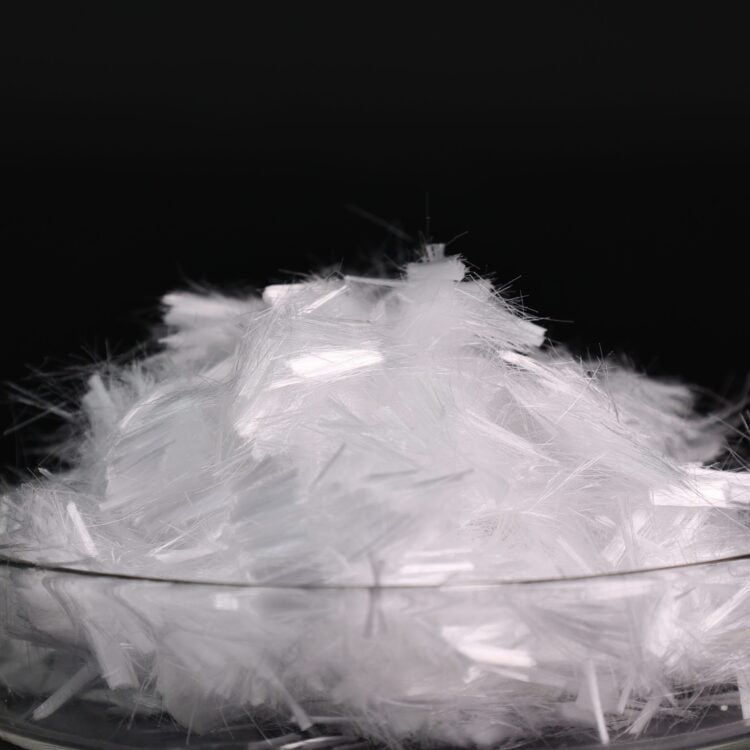
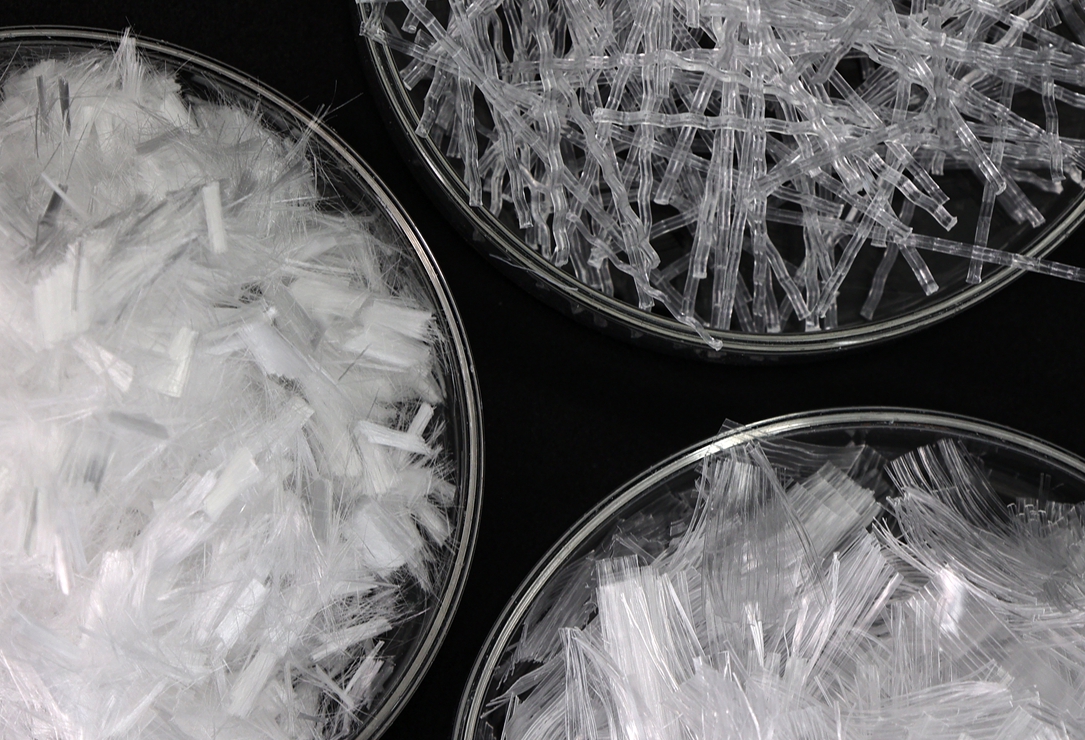
Synthetic fibers are commonly used as reinforcement in concrete to improve its properties, such as crack resistance, durability, and impact strength. They are an alternative or supplement to traditional steel reinforcement, offering several advantages like corrosion resistance, easier handling, and faster installation.
| Synthetic Fibre | PPMF | SD0136 | Polypropylene Macro Fiber(PPMF) |
| PPSF | SD0135 | Polypropylene Mesh Fiber(PPSF) | |
| PPCF | SD0062 | Polypropylene Chopped&Monofilament Fibre(PPCF) | |
| PVAF | SD0194 | polyvinyl alcohol Fiber | |
| PANF | SD0195 | Polyacrylonitrile Fiber |
Types of Synthetic Fibers used in Concrete:
- Polypropylene Fibers:
- Most common synthetic fibers used in concrete.
- Help control plastic shrinkage cracking.
- Improve impact and abrasion resistance.
- Do not corrode.
- Polyacrylonitrile Fiber:
- Provide good flexibility and toughness.
- Used for crack control and as a supplementary reinforcement.
- Polyethylene Fibers:
- Have high tensile strength.
- Improve fracture toughness and durability.