gypsum mortar workability

Gypsum-based lightweight plastering mortar is a dry-mix mortar primarily composed of β-hemihydrate gypsum as the cementitious binder, supplemented with lightweight aggregates, functional fillers, and chemical additives. While offering advantages such as lightweight properties, fire resistance, and humidity regulation, this material system also presents common challenges during actual application, including high viscosity, significant scraping resistance, and difficulty in finishing.
Systematically improving its workability hinges on precisely controlling the mortar’s rheological behavior through specialized chemical additives.
I. Rheological Roots of Core Challenges
The poor workability of gypsum-based mortar fundamentally stems from its suboptimal rheological properties:
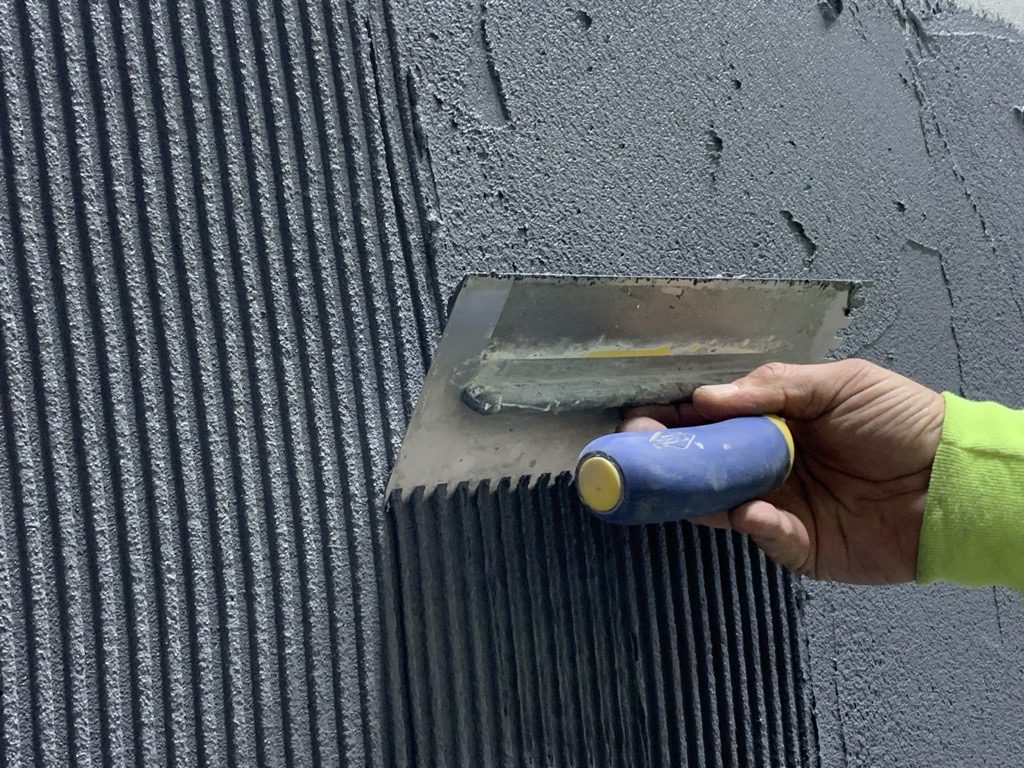
High yield stress: Results in excessive resistance during initial application, manifesting as a “heavy” feel.
Rapid thixotropic recovery: The window for mortar to thin after mixing is too brief, hindering spreading and finishing operations.
High interparticle friction: Direct contact between gypsum and other powder particles without lubrication causes construction stickiness.

II. Solution: Rheology-Modifying Additive Technology
To address these issues, polymer additives with specialized molecular designs (e.g., SidleyChem‘s MP-22M01) represent a proven effective technical approach. Their mechanism of action primarily manifests in the following aspects:
Steric Hindrance and Lubrication Effects
Additive molecules adsorb onto gypsum particle surfaces, forming an effective polymeric layer. This creates steric hindrance that prevents particle agglomeration while providing superior interparticle lubrication, significantly reducing internal friction during application.
Moisture Regulation
Optimized additives enhance the system’s water retention and moisture distribution, ensuring thorough and uniform gypsum hydration. This prevents quality issues like surface powdering and cracking, thereby extending the mortar’s effective working time.
III. Conclusion
The introduction of specialized rheology-modifying additives fundamentally reshapes the workability of gypsum-based lightweight plastering mortar. This technical approach not only resolves the challenges of high viscosity and difficult application but also enhances mortar stability and ease of use, providing reliable technical support for ensuring construction quality and improving operational efficiency.




















