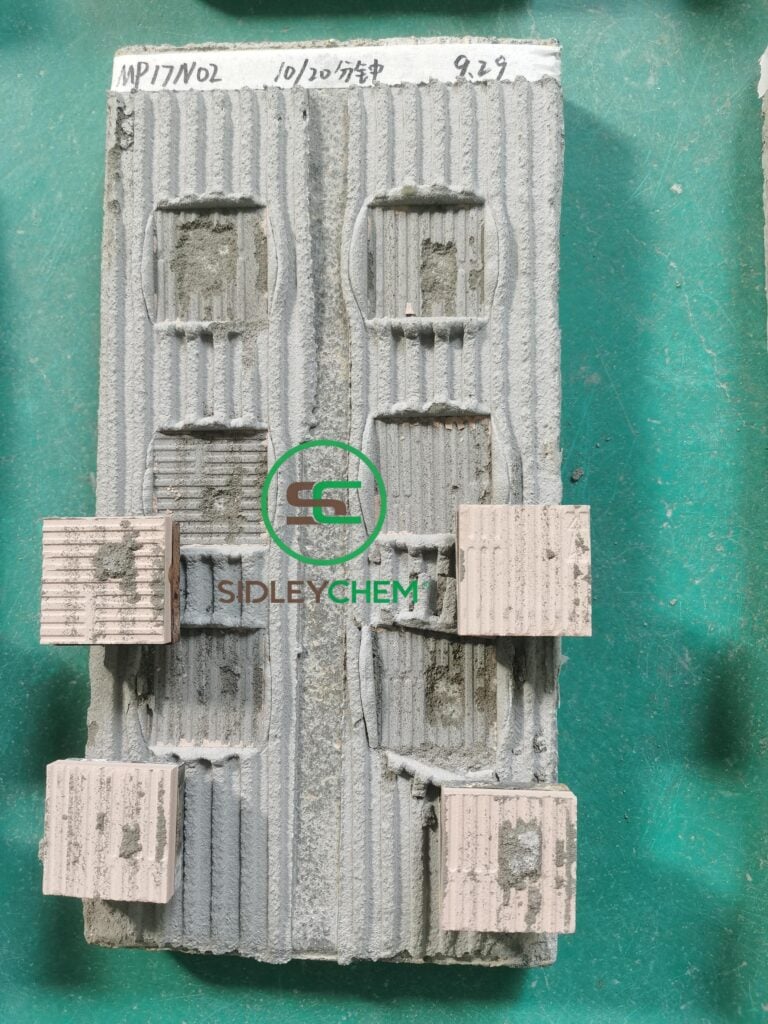
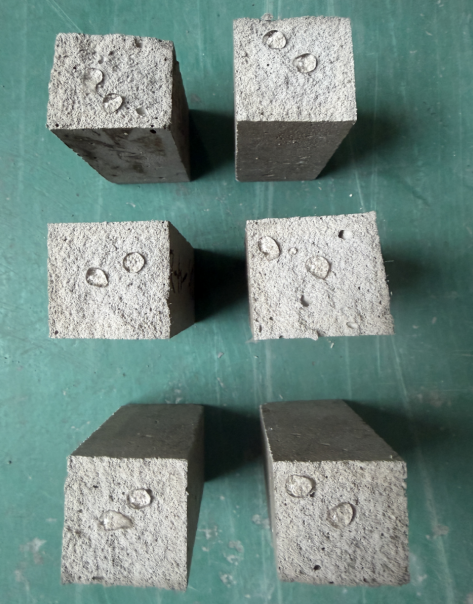
Dry-mix mortar shrinkage reducing admixture
Shrinkage Reducing Admixtures (SRA), as key performance-enhancing additives, precisely control internal moisture migration and interfacial forces within mortar. They effectively inhibit shrinkage deformation, making them a core material for elevating the performance of dry-mix mortars.
I. Mechanism of Action and Product Advantages
1. Mechanism of Action
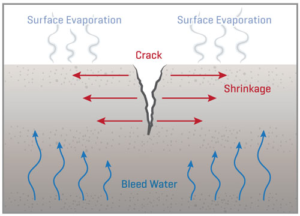 SRA primarily function by lowering the surface tension of the capillary pore solution, thereby reducing the stress induced by water loss and shrinkage. They also increase the viscosity of pore water, strengthen the adsorption of water molecules, and inhibit contraction.
SRA primarily function by lowering the surface tension of the capillary pore solution, thereby reducing the stress induced by water loss and shrinkage. They also increase the viscosity of pore water, strengthen the adsorption of water molecules, and inhibit contraction.
Furthermore, they optimize cement hydration, reducing shrinkage caused by incomplete hydration. Some products can also slow down moisture evaporation, ensuring more complete hydration.
2. Product Advantages
-
Significantly reduce drying shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage, minimizing risks of cracking, hollowing, and leakage to enhance durability.
-
Do not adversely affect, or only mildly affect, initial setting time and early strength, ensuring construction safety and structural integrity.
-
Powder form facilitates easy blending with dry-mix components, making them ideal for industrialized precise batching and mass production.
II. Applicable Scenarios
SRA are applicable across both ordinary and specialty dry-mix mortars, proving indispensable in engineering scenarios with stringent shrinkage control requirements. Specific applications include:
-
Floor leveling/screed mortars
-
Repair and reinforcement mortars
-
Specialty functional mortars
-
Ordinary building mortars (e.g., masonry, plastering)

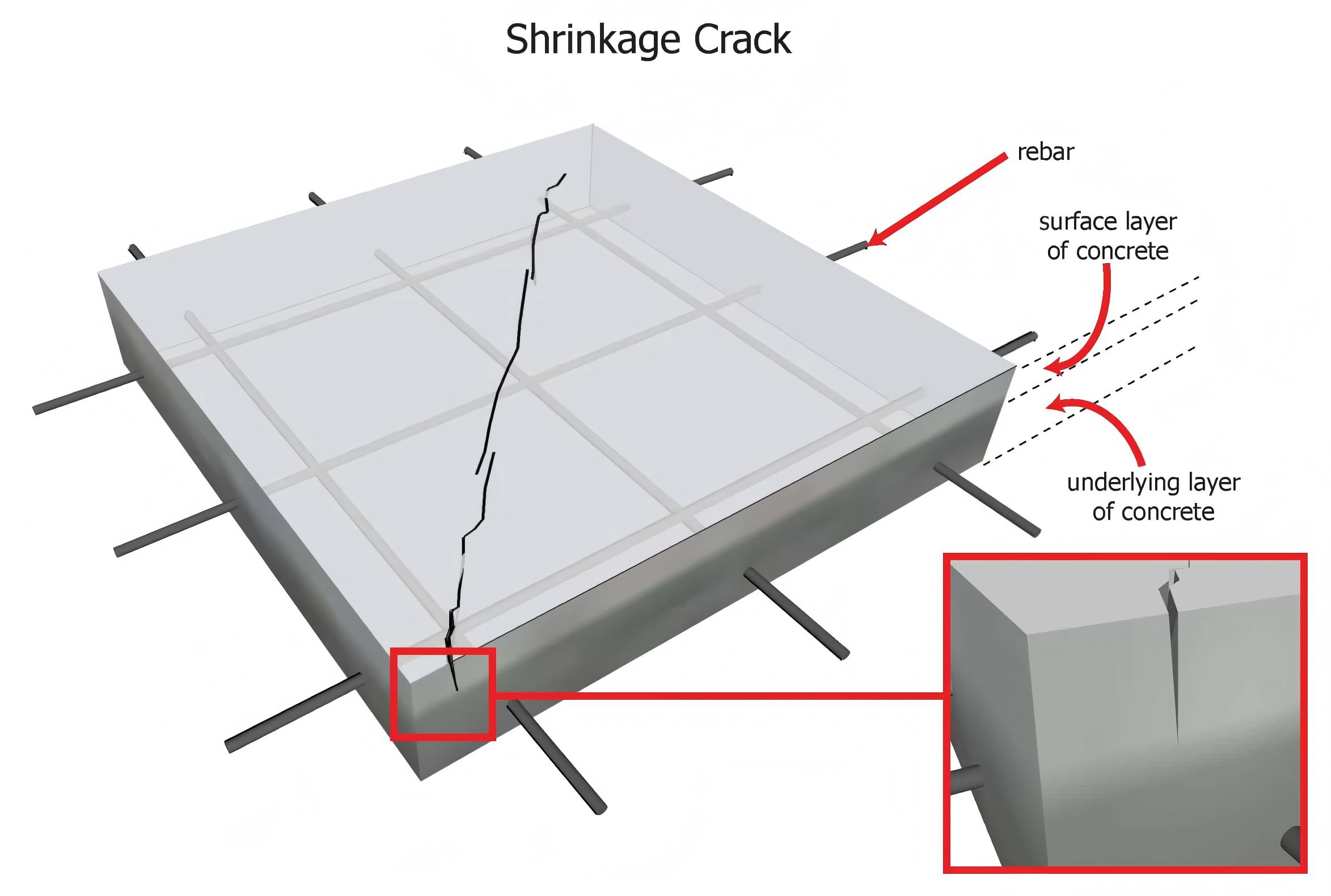
III. Key Technical Application Points
Product Selection & Form Compatibility
The pre-mixed nature of dry-mix mortars necessitates additives with excellent dry-powder compatibility and dispersion stability. Therefore, powdered SRAs are the preferred choice. These typically use inorganic materials as carriers, with active components being organic alcohols or polyol ether derivatives. They offer advantages such as low VOC, ease of uniform mixing with dry components, and superior stability during storage and transportation. While liquid SRAs are effective, they require specialized liquid dosing systems and can compromise the storage stability of dry-mix products, limiting their use to special custom formulations.
2.Reasonable control of dosage

3.Mixing & Application Process Optimization
Powdered SRA must be thoroughly mixed with cementitious materials and fine aggregates during the dry-mix production phase. Standard mixing equipment is recommended to ensure uniform dispersion and prevent localized high or low concentrations that could affect performance consistency.
During application, strictly control the mixing water content, adhering to the “little and often” principle to avoid excess water exacerbating later-stage shrinkage. The ambient temperature should ideally be maintained between 10°C and 30°C. Avoid application under conditions of high-temperature exposure or freeze-thaw cycles. Post-application, follow standard curing procedures to ensure complete mortar hydration.
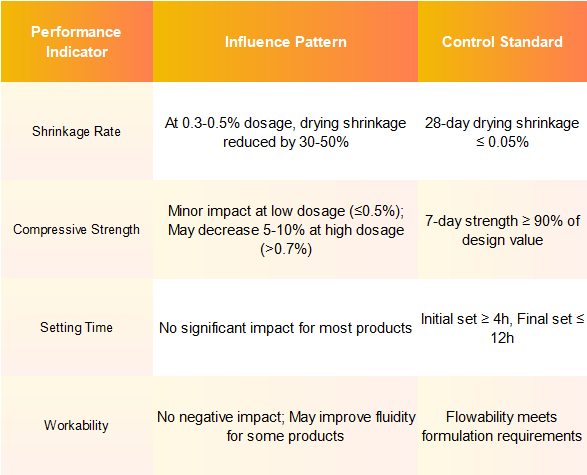
IV.Performance Impact & Production Control Metrics
V. Common Issues & Solutions

VI. Recommended Products & Reference Formulations
1. Recommended Product
-
Sidleychem SR-100P (Organic Alcohol-based Powder): Recommended dosage 0.4-0.7%. Suitable for self-leveling compounds and floor screeds.
2. Typical Reference Formulation
-
Self-Leveling Compound (Dry mix per 100 kg):
-
Ordinary Portland Cement: 45 kg
-
Quartz Sand: 50 kg
-
Fly Ash: 3 kg
-
Cellulose Ether: 0.3 kg
-
Redispersible Polymer Powder (RDP): 1.5 kg
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): 0.4 kg
-
Superplasticizer: 0.2 kg
-




















