ETICS adhesive mortar additives
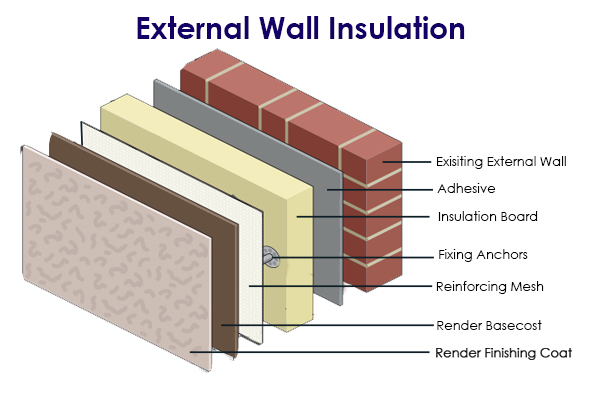
The External Insulation and Finish System (EIFS), commonly known in Europe as the External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS), has become a key technology globally for enhancing building energy efficiency and ensuring occupant comfort. By applying multiple composite layers to form a continuous insulation envelope on the building’s external facade, the system effectively minimizes thermal bridging and reduces energy consumption.
System Composition and The Critical Role of Adhesive Mortar
A typical ETICS consists of the following layers:
-
Substrate
-
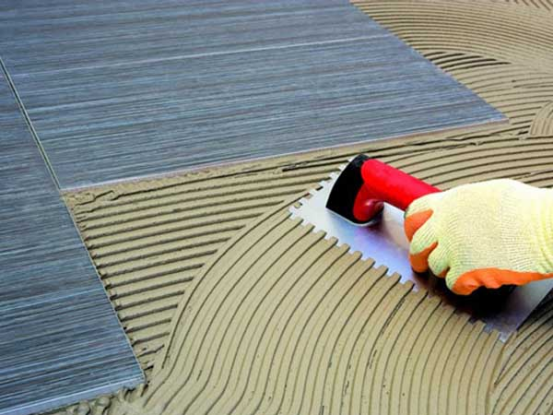
Adhesive Layer – The adhesive mortar.
-
Insulation Layer – Typically Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) boards.
-
Reinforcing Layer – Base coat mortar with embedded glass fiber mesh.
-
Finish Layer – Coatings or decorative renders.
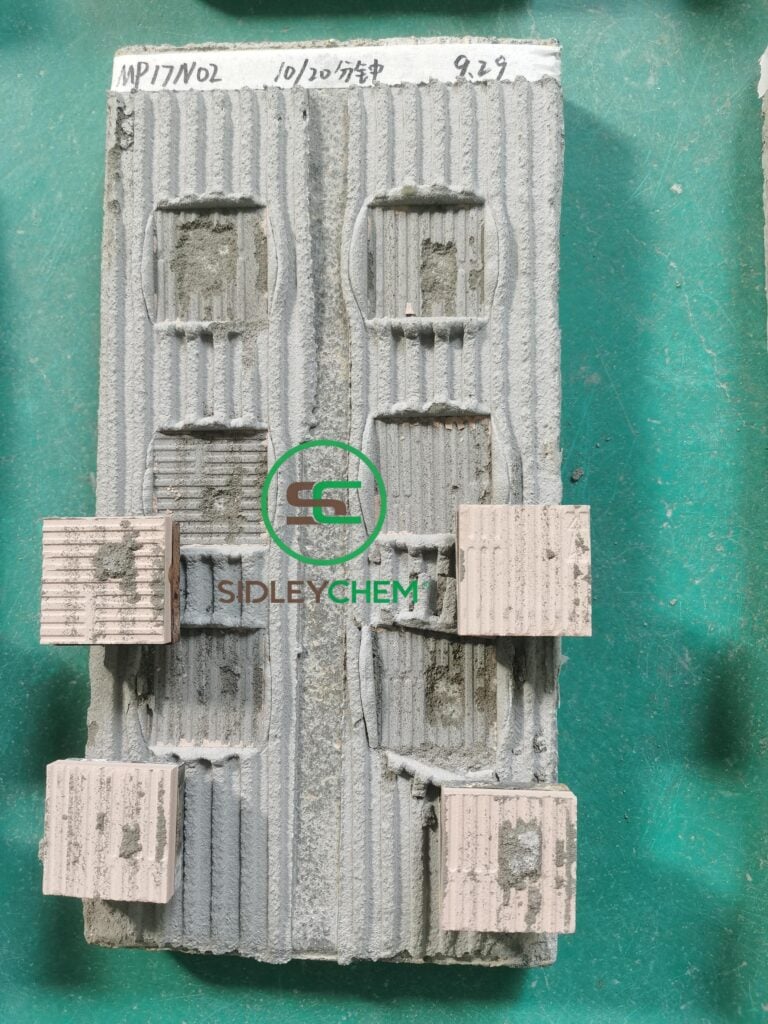
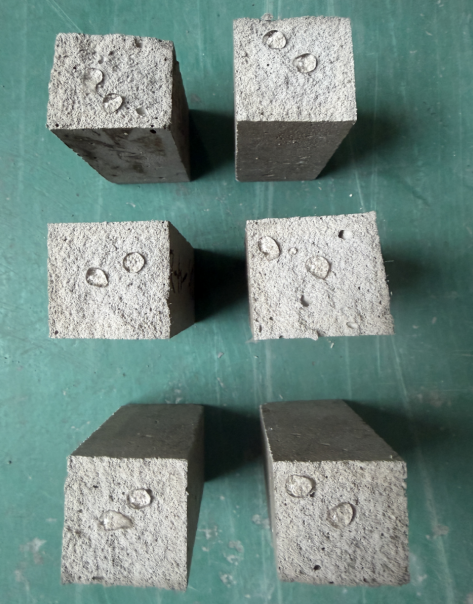
The adhesive mortar, as the critical material bonding the substrate to the insulation boards, directly determines the long-term safety and durability of the entire system. Composed mainly of cement, graded aggregates, functional polymer additives (such as cellulose ethers and Redispersible Polymer Powder), and hydrophobic agents, it must simultaneously meet multiple requirements: high bond strength, excellent flexibility, good workability, and sufficient open time.
Key Performance Requirements and Challenges for Adhesive Mortar
To ensure the long-term performance of ETICS under various climatic conditions, adhesive mortar must overcome the following challenges:
-
High Initial Adhesion & Flexibility: It must firmly secure insulation boards while accommodating differential movement between the substrate and insulation material caused by temperature and humidity changes, preventing cracking or delamination.
-
Excellent Weather Resistance & Hydrophobicity: It must withstand long-term exposure to rain, freeze-thaw cycles, and UV radiation, protecting the system from water ingress.
-
Good Workability: It must possess suitable consistency, anti-sag properties, and sufficient open time to facilitate thin-bed or ribbon application.

SidleyChem High-Performance Adhesive Mortar Solutions
 Addressing these technical challenges, SidleyChem offers a range of globally proven high-performance additives for formulating adhesive mortars that meet the most stringent standards.
Addressing these technical challenges, SidleyChem offers a range of globally proven high-performance additives for formulating adhesive mortars that meet the most stringent standards.
-
Cellulose Ethers (for Water Retention & Thickening)
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose (HEMC): e.g., ME 34N01/02, provides excellent workability, water retention, and a smooth application feel.
-
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC): e.g., MP 34N01/02, widely used in various mortars for its good water retention, thickening effect, and cost-performance ratio.
-
-
Redispersible Polymer Powder (RDP) (for Adhesion & Flexibility)
-
Economy Grade: RDP 7028, suitable for standard, cost-sensitive projects.
-
Standard Grade: RDP 66143, 66153, 7053, 7033, offering excellent bond strength, flexibility, and water resistance, meeting most national standards.
-
High-Performance Grade: RDP 86353, designed for extremely high bond strength, impact resistance, and application under demanding conditions.
-
-
Silicone Hydrophobic Powder(for Enhanced Water Resistance)
-
WS 80, WS 90: High-efficiency silicone-based hydrophobic agents. They significantly reduce mortar water absorption, improve the system’s long-term weather resistance and freeze-thaw durability, without compromising breathability.
-




















