Detergent formulation ingredients
For manufacturers of fast-moving consumer goods, the selection of raw materials directly determines the performance, safety, and market competitiveness of the final product. Faced with a vast array of chemicals, how does one make a scientific choice? This article systematically outlines ten key raw materials used in detergents, personal care, and other FMCG products, explains their functions, and provides crucial selection and application guidance to offer clear direction for your formulation development.
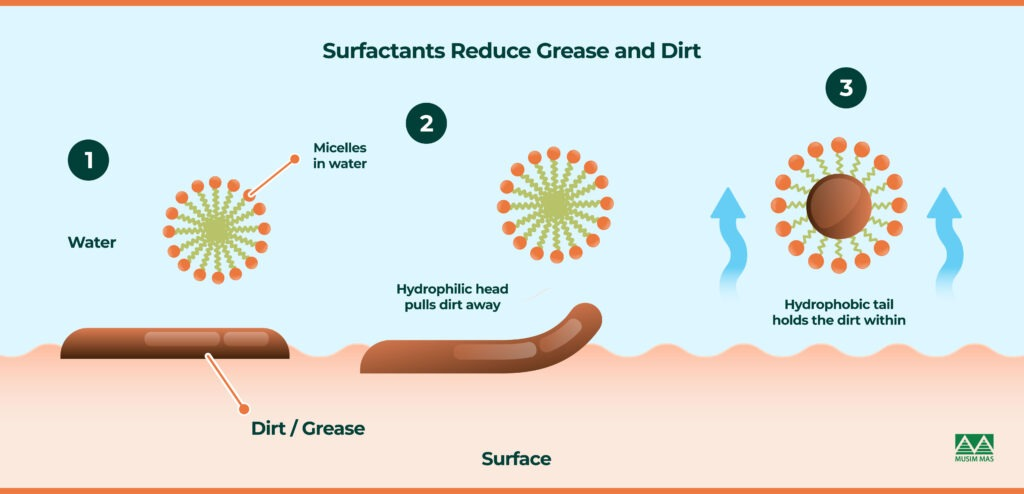
I. Functional Analysis of Ten Key Raw Materials

-
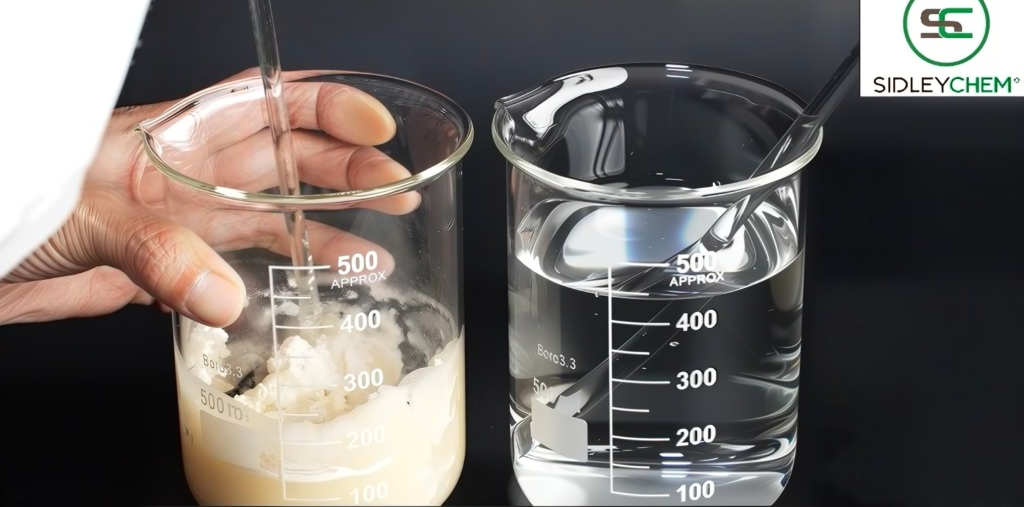
Sulfonic Acid & Derivatives: As anionic surfactants, they possess excellent detergency, wetting, and emulsifying power. They serve as fundamental components in laundry powders, dishwashing detergents, and industrial cleaners.
-
AES (Sodium Laureth Sulfate): A high-performance anionic surfactant known for its strong detergency and foaming power. Widely used in liquid detergents, process control is needed to prevent gel formation.
-
AEO-9 (Alcohol Ethoxylate): A classic non-ionic surfactant renowned for its outstanding emulsifying, dispersing, water-soluble, and cleaning properties. It is a key ingredient in various cleaning agents and textile/printing auxiliaries.
-
6501 (Cocamide DEA): A non-ionic surfactant primarily used as a thickening and foam stabilizer. It significantly enhances the richness and persistence of foam in a system and improves cleaning efficacy.
-
Cocamidopropyl Betaine (e.g., BS-12): An amphoteric surfactant valued for its mildness, excellent cleaning, antistatic properties, and hardness tolerance. It is an ideal choice for formulating premium shampoos and body washes.
6.Flake Caustic Soda (Sodium Hydroxide): An essential basic chemical raw material. In the FMCG sector, it is commonly used to adjust pH and is a necessary component in many cleaning agent formulations.
 7.Industrial Salt (Sodium Chloride): In some low-cost formulations, it can function as an inorganic salt thickener, effectively increasing the apparent viscosity of liquid products.
7.Industrial Salt (Sodium Chloride): In some low-cost formulations, it can function as an inorganic salt thickener, effectively increasing the apparent viscosity of liquid products.
8.FMCG Fragrances: Scents such as lemon or floral are used to impart pleasant odors, enhancing the sensory experience. Selection must align with market preferences and regulatory requirements.

9.Functional Additives: This category includes solubilizers (ensuring ingredient compatibility), preservatives (ensuring shelf-life safety), and colorants (adjusting product appearance). They are key to perfecting formulation performance and compliance.
10.HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose): An efficient rheology modifier and stabilizer. It significantly thickens and prevents formulation separation or thinning. In shampoos and body washes, it provides a smooth, delicate texture and ensures long-term storage stability.
II. Key Recommendations for Selection and Application
-
Compliance First: All raw materials must comply with national regulations and standards and those of the target market. This is the prerequisite for safe product launch.
-
Safety and Market Orientation: Pay attention to the toxicological data and ecological requirements of ingredients. Given that some consumers may have sensitivities to fragrances or preservatives, “additive-free” or “minimalist” formulations represent an important market segment.
-
Start Simple and Scale Up: For formulation beginners, it is advisable to start with a combination of 2-3 core surfactants, gradually gaining experience before expanding to functional additives for performance optimization.




















