Expanding Agent vs Shrinkage Reducing Admixture
As key chemical admixtures for controlling volume change and inhibiting cracking in concrete, expanding agents and shrinkage reducing admixtures (SRAs) are both critical. However, they function in fundamentally opposite ways. Their core distinctions are outlined in the following aspects.
1. Mechanism of Action
-
 Expanding Agent: Works by undergoing a chemical reaction (e.g., formation of ettringite) during the concrete hardening process to generate controlled expansion, thereby compensating for autogenous and drying shrinkage.
Expanding Agent: Works by undergoing a chemical reaction (e.g., formation of ettringite) during the concrete hardening process to generate controlled expansion, thereby compensating for autogenous and drying shrinkage.
-
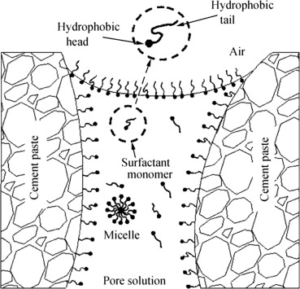
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): Functions by reducing the surface tension of pore water within the concrete’s capillary pores. This lowers the meniscus pressure and slows the rate of moisture migration, effectively inhibiting plastic, autogenous, and drying shrinkage from occurring.

2. Impact on Shrinkage Types & Crack Control Efficacy
-
Expanding Agent: Primarily compensates for autogenous and drying shrinkage, with a weaker effect on controlling early-age plastic shrinkage cracking. Tests show that a 12% dosage can reduce 28-day autogenous shrinkage by 62.8% and drying shrinkage by 39.8%.
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): Significantly inhibits plastic, autogenous, and drying shrinkage. For example, a 2% dosage can reduce 28-day autogenous shrinkage by 83.7% and drying shrinkage by 49%. It offers superior control over plastic shrinkage cracking, with a cracking index of 0 at a 2% dosage.
3. Dosage & Cost-Effectiveness
-
Expanding Agent: Typical dosage is 8%-12% by cement mass, resulting in higher cost.
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): Lower typical dosage, usually 0.5%-2% by cement mass. With technological advances, costs have decreased significantly, offering better economic efficiency.
4. Suitable Application Scenarios
-
Expanding Agent: Ideal for mass concrete, shrinkage-compensating structures (e.g., closure pours, water-proofing engineering).
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): More suitable for applications highly sensitive to early-age cracking, such as high-performance concrete, pumped concrete, and concrete pavements where shrinkage cracks must be strictly controlled.

5. Technical Advantages
-
Expanding Agent: Offers excellent long-term impermeability but is highly dependent on adequate curing.
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): Highly effective against early-age plastic and autogenous shrinkage, with broad applicability.
6. Usage Considerations
-
 Expanding Agent: Over-dosage may cause expansion cracking, requiring strict dosage control.
Expanding Agent: Over-dosage may cause expansion cracking, requiring strict dosage control.
-
Shrinkage Reducing Admixture (SRA): Higher dosages do not negatively affect volumetric stability but require ensuring uniform dispersion in the mix.
In conclusion, selecting and applying the appropriate admixture—whether an expanding agent or an SRA—based on the specific cracking challenges is essential for achieving optimal performance in concrete structures.




















