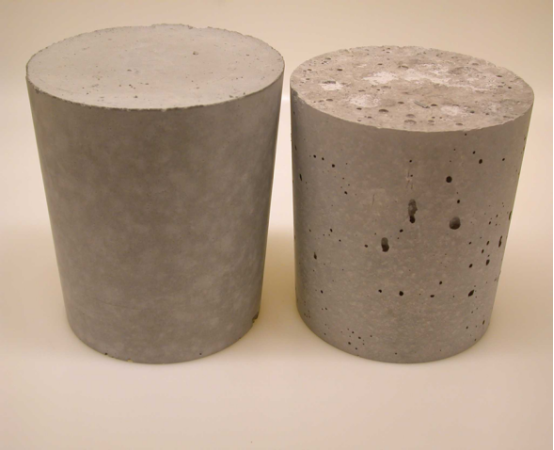
water reduction rate measurement

Water-Reducing Agent are admixtures added before or during concrete mixing that can reduce or significantly decrease the water content in the concrete mixture. Incorporating Water-Reducing Agent into concrete effectively improves workability and fluidity, enhances the concrete structure, and increases strength. When maintaining the same concrete strength, they can also save a substantial amount of cement. Therefore, Water-Reducing Agent have become an indispensable admixture in concrete formulation.
I. Three Methods to Determine the Water Reduction Rate
In practical applications, how can we determine the water reduction rate of Water-Reducing Agent? Currently, the water reduction rate of Water-Reducing Agent can be summarized into three types: paste water reduction rate, mortar water reduction rate, and concrete water reduction rate. All these methods can assess the water reduction rate of Water-Reducing Agent, but they differ significantly and have poor correlation.
II. Water Reduction Rate Performance Under Different Testing Methods
Paste Water Reduction Rate: This refers to the water reduction rate of the water reducer in a cement paste. The water reducer directly disperses cement particles through electrostatic repulsion and steric hindrance. At this stage, without interference from aggregates, the dispersion effect is more direct, and the water reduction rate is typically the highest. It primarily depends on the adsorption strength between the water reducer’s molecular structure and the cement particles. 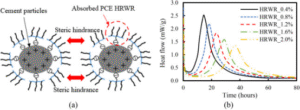 For example, our company’s polycarboxylate-based high-range water reducer PCE154L, utilizing the steric hindrance of side chains and electrostatic repulsion of the main chain, significantly reduces the solid-liquid interface energy, achieving a paste water reduction rate of over 35%.
For example, our company’s polycarboxylate-based high-range water reducer PCE154L, utilizing the steric hindrance of side chains and electrostatic repulsion of the main chain, significantly reduces the solid-liquid interface energy, achieving a paste water reduction rate of over 35%.

Mortar Water Reduction Rate: This is the water reduction rate of the water reducer in mortar. Due to the incorporation of fine aggregates, the water reduction rate is lower than that in paste. The specific surface area and porosity of the aggregates adsorb part of the water reducer, reducing its effective concentration. However, by optimizing the dosage of the water reducer, fluidity and strength can still be significantly improved. For example, our company’s polycarboxylate-based high-range water reducer PCE154L can achieve a mortar water reduction rate of up to 30%.
Concrete Water Reduction Rate: This is the water reduction rate of the water reducer in concrete. Due to the presence of coarse aggregates and complex interfacial interactions, the water reduction rate further decreases. Polycarboxylate-based Water-Reducing Agent, owing to the slow-release effect of their branched chains, can better maintain slump, but the weakening of the dispersion effect by aggregates is more pronounced, yet they can still demonstrate a considerable water reduction rate. For example, our company’s polycarboxylate-based high-range water reducer PCE154L can achieve a concrete water reduction rate of over 25%.
III. Cause Analysis of Water Reduction Rate Differences and Application Strategies
Theoretical analysis shows that from paste → mortar → concrete, the increasing proportion of aggregates leads to a decrease in the effective concentration of the water reducer, resulting in a gradual reduction in the water reduction rate. Electrostatic repulsion dominates in paste and mortar, while concrete requires a balance between steric hindrance and lubrication of aggregate interfaces. Concrete focuses more on slump retention and strength enhancement, whereas paste emphasizes dispersion efficiency. Therefore, the performance of paste, mortar, and concrete water reduction rates varies, with the rate descending in the order: paste > mortar > concrete. These differences stem from material complexity and the intensity of interfacial interactions. In practical applications, it is necessary to adjust the type and dosage of Water-Reducing Agent according to the specific system. For instance, polycarboxylate-based Water-Reducing Agent are preferred in concrete to balance water reduction rate and slump retention. Alternatively, water-reducing type Water-Reducing Agent, slump-retaining type Water-Reducing Agent, and/or comprehensive type Water-Reducing Agent can be reasonably combined to obtain an ideal high-efficiency water reducer.
IV. SidleyChem Product Portfolio and Solutions
Currently, our company offers various types of Liquor Water Reducer, including the water-reducing type PCE154L, PCE156L; the slump-retaining type PCE155L, PCE157L; the early-strength type PCE159L; and the workability-adjusting type PCE150L. For different types of concrete such as ready-mix concrete, precast concrete, high-fluidity concrete, and low-slump concrete, one or more of the above mother liquids can be rationally combined to obtain the desired functional water reducer, ultimately producing high-quality concrete.




















