Choosing concrete expanding agents
1. Core Function & Principle
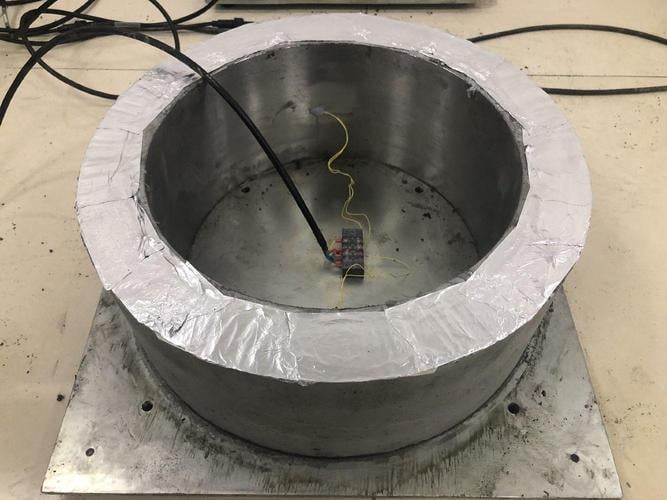
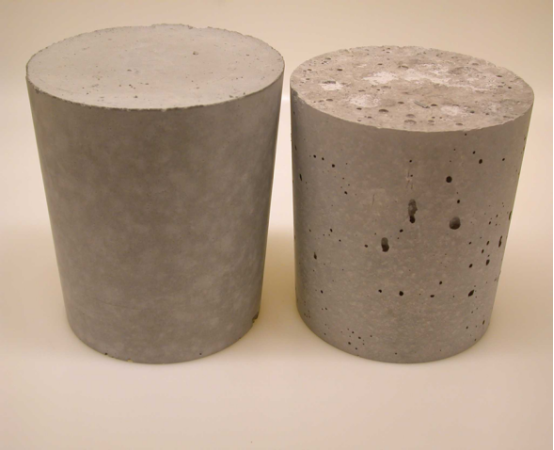
 A concrete expanding agent is a functional chemical admixture. When added to concrete, it undergoes a hydration reaction that generates controlled volumetric expansion. This expansion is designed to counteract the shrinkage stresses (from drying, cooling, or cement hydration) that occur during concrete hardening. Its primary purposes are to prevent cracking, improve impermeability and density, and enhance interfacial bonding.
A concrete expanding agent is a functional chemical admixture. When added to concrete, it undergoes a hydration reaction that generates controlled volumetric expansion. This expansion is designed to counteract the shrinkage stresses (from drying, cooling, or cement hydration) that occur during concrete hardening. Its primary purposes are to prevent cracking, improve impermeability and density, and enhance interfacial bonding.
Essentially, it uses “controlled expansion” to achieve shrinkage compensation or induce self-stress, meeting diverse engineering needs for crack resistance, waterproofing, and seamless construction.
2. Main Types & Mechanism Comparison
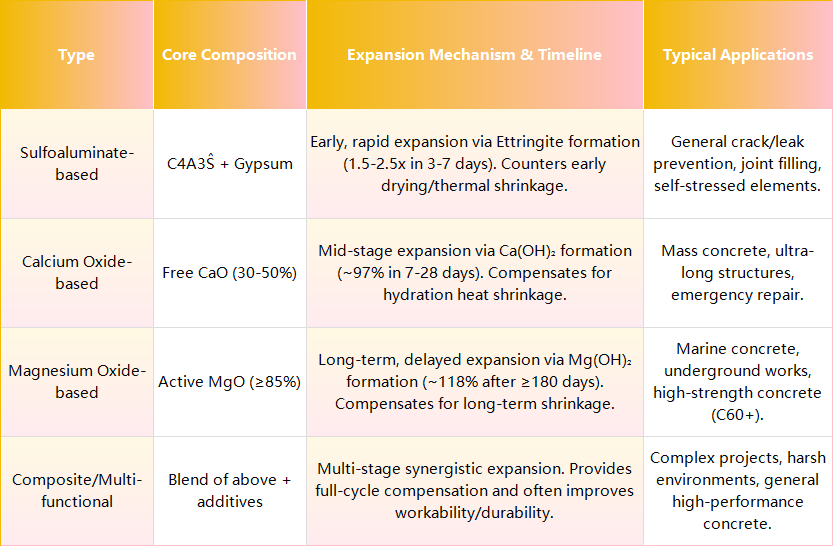
The performance of an expanding agent depends largely on its core chemical composition. The following table summarizes the four main types, their mechanisms, and key application areas:
3. Application Guidance & Dosage
Selecting the correct type and dosage is critical for success and cost-effectiveness.
-
Dosage Range (by cement weight):
-
-
CaO-based: 3%-8% (5%-8% for mass concrete).
-
MgO-based: 4%-10% (6%-10% for marine works).
-
Composite: 5%-12% (varies by formulation).
- Sulfoaluminate-based: 6%-12% (8%-10% for crack control).
-

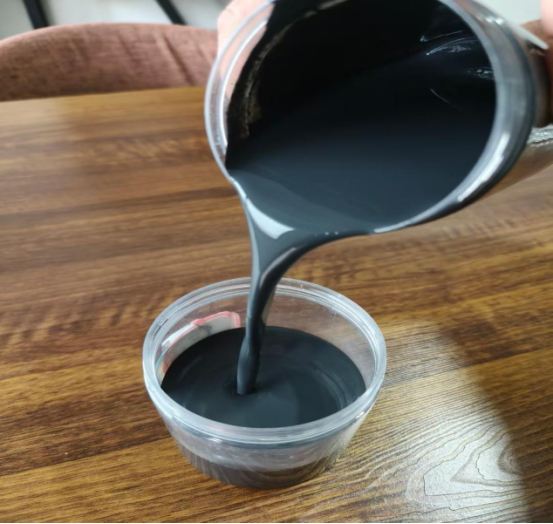
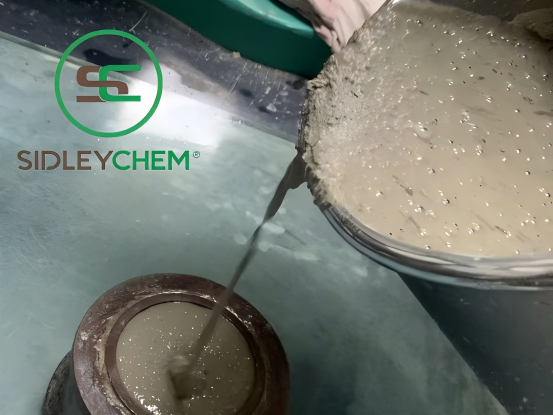
4. SidleyChem’s Innovative Solution: SIDLEY EAMP
 To address the demands of modern underground and marine structures, SidleyChem has developed SIDLEY EAMP, a next-generation composite expanding agent masterbatch.
To address the demands of modern underground and marine structures, SidleyChem has developed SIDLEY EAMP, a next-generation composite expanding agent masterbatch.
-
Production Efficiency: 1 ton of SIDLEY EAMP produces 2-4 tons of the finished product, SIDLEY EA25.
-
Recommended Dosage:
-
For SIDLEY EA25: Use 4.0% – 8.0% by weight of total cement.
-
For SIDLEY EAMP (direct use): Use 1.0% – 2.0% by weight of total cement.
-
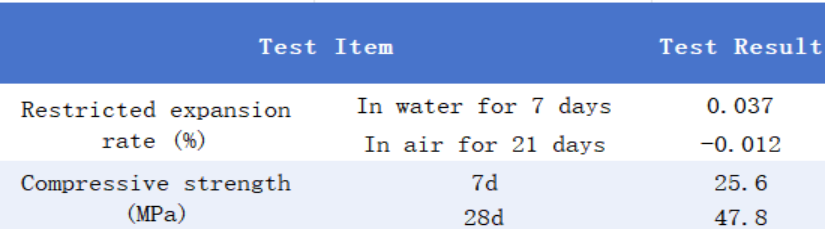
The table below presents key test data for our expanding agent series.